
Aug . 04, 2024 02:56 Back to list
Understanding the Functionality and Applications of Differential Pressure Gauges in Various Industries
Understanding Differential Pressure Gauges and Their Service
Differential pressure gauges are critical tools extensively employed across various industries to measure the difference in pressure between two points within a system. These gauges are essential for monitoring the performance and operation of equipment, ensuring safety, and optimizing processes in a range of applications, from HVAC systems to chemical processing plants.
What Are Differential Pressure Gauges?
Differential pressure gauges work by comparing the pressure at two separate locations and displaying the difference as a readable value. The operation involves two pressure connections one for the higher pressure and one for the lower pressure. This configuration allows the gauge to provide accurate readings even in fluctuating conditions. They can be analog or digital, with the latter often featuring advanced capabilities such as data logging and remote monitoring.
Applications of Differential Pressure Gauges
1. HVAC Systems In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, differential pressure gauges help monitor air filters, ductwork, and fan performance. By providing real-time data, they allow for proactive maintenance and ensure optimized air flow, which is crucial for energy efficiency and indoor air quality.
2. Process Industries In industries such as oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and food processing, these gauges are used to monitor pressure across filters, separators, and vessels. This information is vital for maintaining efficiency and preventing equipment failure or process upsets.
3. Water Treatment Differential pressure gauges are pivotal in water treatment facilities, where they monitor pressures across filters and membranes. By doing so, they help operators maintain optimal performance and prevent clogging, which can lead to costly downtime.
differential pressure gauges service
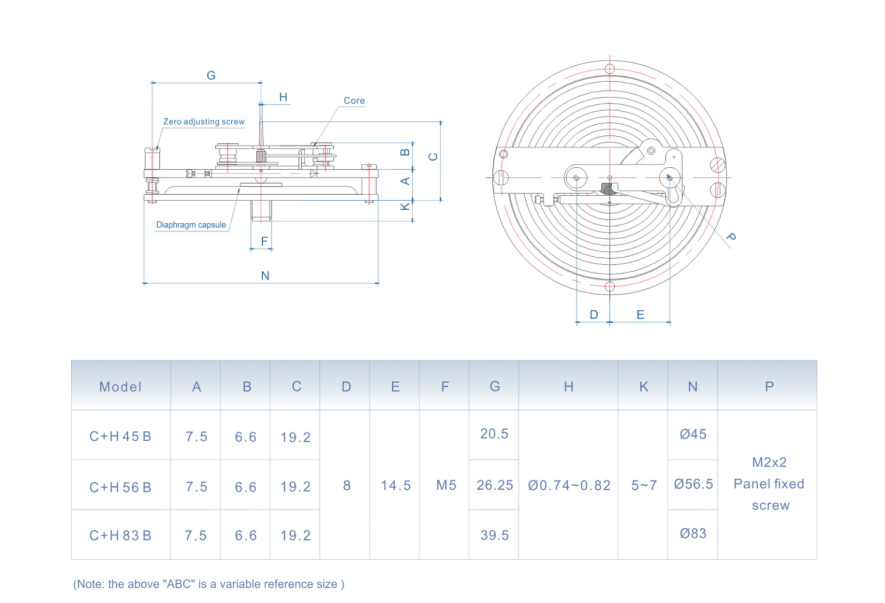
Maintenance and Calibration
The operation of differential pressure gauges relies on accurate readings, emphasizing the importance of regular maintenance and calibration. Calibration assures that the gauge readings are correct, and should be performed periodically or after any repairs. Maintenance practices may include inspecting the gauge for leaks, checking connections, and ensuring that the sensing elements are clean and unobstructed.
Selecting the Right Gauge
When selecting a differential pressure gauge, consider factors such as the pressure range, material compatibility, environmental conditions, and the required accuracy. Gauges are available in various designs, including diaphragm, capsule, and bourdon tube types, each suited for different applications. For instance, diaphragm gauges are often preferred for measuring low pressures and are particularly effective in corrosive environments due to their robust construction.
The Impact of Digital Technology
With technological advancements, digital differential pressure gauges have gained popularity. These devices offer enhanced features such as programmable alarms, digital displays, and connectivity options for integration with control systems. The ability to communicate with other devices and systems allows for more comprehensive monitoring and automation, significantly improving operational efficiency and safety.
Conclusion
Differential pressure gauges are indispensable instruments in various fields, playing a crucial role in ensuring efficiency, safety, and reliability in operations. As industries continue to evolve, the importance of these gauges and their proper service cannot be overstated. Regular maintenance and calibration are essential to keeping these instruments functioning correctly, thus preventing costly outages and ensuring the optimal performance of systems reliant on accurate pressure measurements. By understanding the applications, maintenance needs, and technological advancements associated with differential pressure gauges, organizations can leverage these tools to enhance their operations effectively.
-
High-Precision 5 Valve Manifold Differential Pressure Gauge Suppliers
NewsApr.29,2025
-
High-Precision Diaphragm Vacuum Pressure Gauges Manufacturers & Quotes
NewsApr.29,2025
-
Omega Differential Pressure Gauges High Accuracy & Durability
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Low Pressure Differential Pressure Gauges Precision Solutions & Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Digital Diaphragm Pressure Gaauge Precision Measurement & OEM Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Differential Pressure Gauge China Price High-Accuracy & Best Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
