
11월 . 25, 2024 16:01 Back to list
Calibrating Differential Pressure Gauges for ODM Applications and Enhanced Accuracy
Calibrating Differential Pressure Gauges An Overview
Differential pressure gauges are crucial instruments used in various industries to measure the pressure difference between two points. Commonly employed in applications such as HVAC systems, filtration processes, and fluid flow monitoring, the accuracy of these gauges directly impacts system performance and operational safety. Therefore, ensuring their precision through proper calibration is essential. This article explores the significance of calibrating differential pressure gauges, the processes involved, and best practices to follow.
Understanding Differential Pressure Gauges
Differential pressure gauges operate by measuring the difference in pressure between two points in a system. They can be applied in numerous settings, including liquid levels in tanks, filter differential pressures, and ventilation systems. The gauge consists of two pressure ports one connected to the high-pressure side and the other to the low-pressure side. The reading is provided as a differential pressure value, usually in units such as pascals (Pa), inches of water column (inH₂O), or psi.
Importance of Calibration
Calibration is a critical process that ensures the accuracy and reliability of differential pressure gauges. Over time, gauges can drift from their original readings due to factors such as mechanical wear, environmental conditions, and thermal effects. If left unchecked, these inaccuracies can lead to system inefficiencies, increased energy consumption, and potential safety hazards. Calibration helps correct these deviations, ensuring that the gauge readings reflect true pressure differences.
Moreover, many industries are governed by regulatory standards that require regular calibration of pressure measurement devices. Compliance with these standards not only enhances operational safety but also prevents costly downtimes and penalties associated with non-compliance.
Calibrating Differential Pressure Gauges The Process
The calibration process typically involves the following steps
1. Preparation Before starting the calibration, gather the necessary tools and equipment, including a reference gauge (known for its accuracy), appropriate pressure sources, and calibration software, if applicable. Ensure that the calibration area is clean and free from disturbances.
2. Connect the Gauges Attach the differential pressure gauge to the calibration setup. This usually involves connecting it to a pressure source capable of providing known pressure values, ensuring a proper seal to avoid leaks.
odm calibrating differential pressure gauge
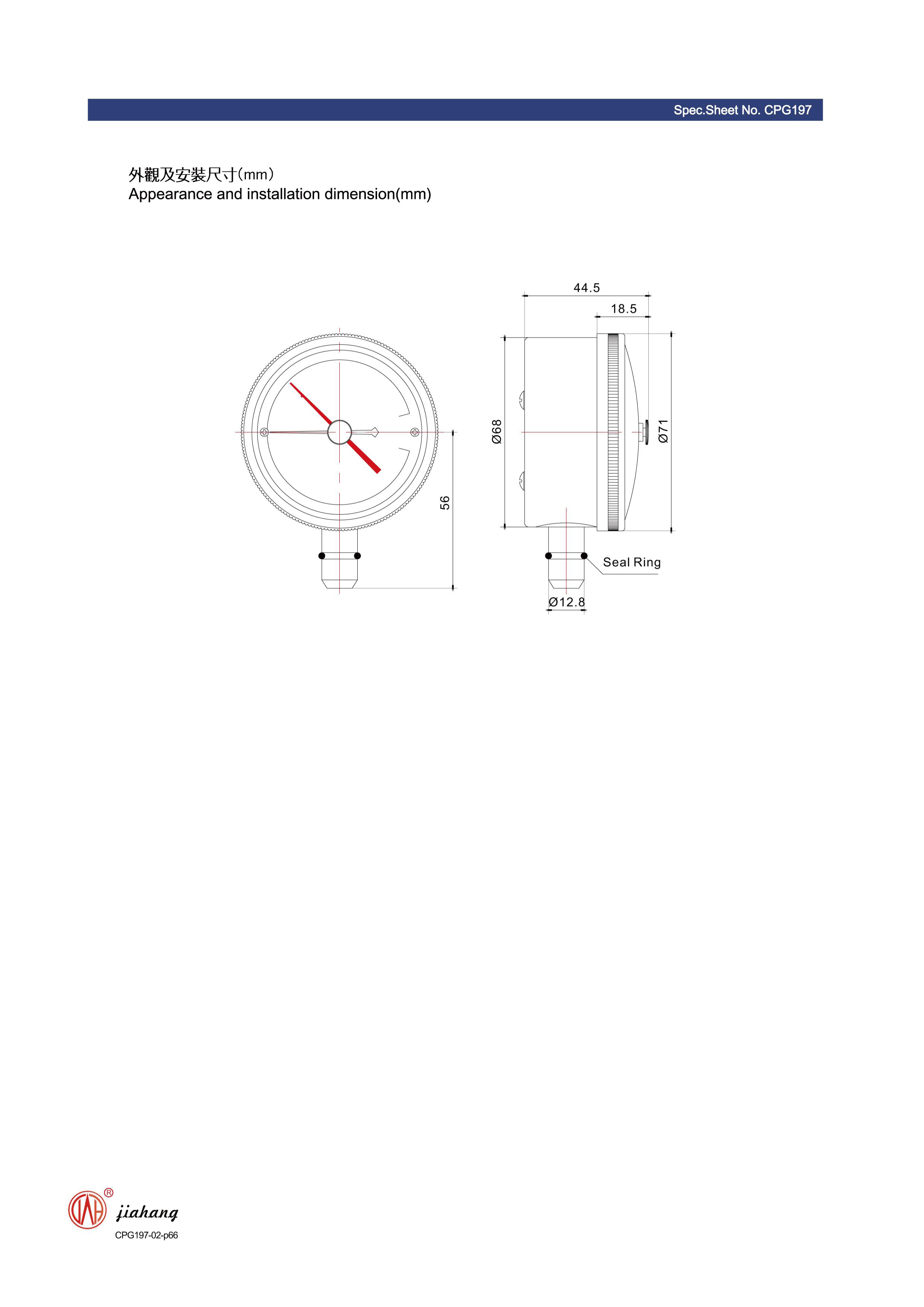
3. Zeroing the Gauge To achieve accurate readings, begin by zeroing the differential pressure gauge at atmospheric pressure. This step ensures that any reading obtained reflects the actual differential pressure rather than atmospheric variations.
4. Applying Known Pressures Gradually apply known pressure values to both sides of the gauge. This can be done using a deadweight tester, pneumatic calibrator, or a similar device. Record the gauge’s readings at various set points, typically at 0%, 25%, 50%, 75%, and 100% of the gauge’s full scale.
5. Comparison and Adjustment Compare the readings from the differential pressure gauge to the reference gauge. Calculate the error at each point and determine if any adjustments are necessary. Many systems allow for electronic calibration adjustments to correct deviations.
6. Documentation Once calibration is complete, document all readings, adjustments made, and any anomalous findings. This record serves as evidence of compliance with calibration protocols and helps in future assessments.
Best Practices for Calibration
1. Regular Intervals Establish a routine schedule for calibrating differential pressure gauges. Depending on usage and environmental conditions, calibration may be needed quarterly, semi-annually, or annually.
2. Ambient Conditions Conduct calibrations in controlled environmental conditions. Variations in temperature and humidity can affect pressure readings.
3. Trained Personnel Ensure that calibration is performed by trained and qualified personnel familiar with both the equipment and the calibration standards.
4. Use of Standards Employ certified and traceable reference gauges to ensure the accuracy of the calibration process. This traceability is crucial for compliance and reliability.
5. Software Integration Consider utilizing calibration management software for scheduling, tracking, and managing calibration records efficiently. Such systems can enhance productivity and ensure compliance with industry standards.
In conclusion, the calibration of differential pressure gauges is a vital practice that ensures accurate pressure measurements across various industrial applications. By adhering to systematic calibration protocols and best practices, organizations can enhance operational efficiency, ensure compliance with regulatory standards, and maintain safety throughout their operations.
-
High-Precision 5 Valve Manifold Differential Pressure Gauge Suppliers
NewsApr.29,2025
-
High-Precision Diaphragm Vacuum Pressure Gauges Manufacturers & Quotes
NewsApr.29,2025
-
Omega Differential Pressure Gauges High Accuracy & Durability
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Low Pressure Differential Pressure Gauges Precision Solutions & Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Digital Diaphragm Pressure Gaauge Precision Measurement & OEM Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Differential Pressure Gauge China Price High-Accuracy & Best Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
