
Oct . 04, 2024 01:19 Back to list
cryogenic differential pressure gauge service
Understanding Cryogenic Differential Pressure Gauge Service
Cryogenic differential pressure gauges play a pivotal role in various industries where low-temperature fluids are handled, such as liquefied natural gas (LNG) facilities, cryogenic storage tanks, and scientific research laboratories. These specialized instruments are designed to measure the pressure difference between two points in a system at extremely low temperatures, typically below -150 degrees Celsius (-238 degrees Fahrenheit). Because of their specialized service, these gauges require careful consideration in their selection, installation, and maintenance.
Operational Principles
Differential pressure gauges operate based on the principle of measuring the difference in pressure between two fluid lines. In cryogenic applications, this could involve monitoring the pressure difference in a liquid line versus a vapor line for gases or liquids that are stored at cryogenic temperatures. These gauges are essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of cryogenic systems, as they help detect potential leaks, monitor flow rates, and control the transfer of fluids.
Construction Features
The construction of cryogenic differential pressure gauges is tailored to withstand the demanding conditions of low-temperature environments. Typically, these gauges are made from materials that exhibit low thermal conductivity and are resistant to embrittlement at cryogenic temperatures. Stainless steel and Monel are common materials used in their fabrication. The sensing elements, often diaphragm-based, are designed to provide accurate readings without significant lag, ensuring reliable performance even in fluctuating pressure conditions.
cryogenic differential pressure gauge service
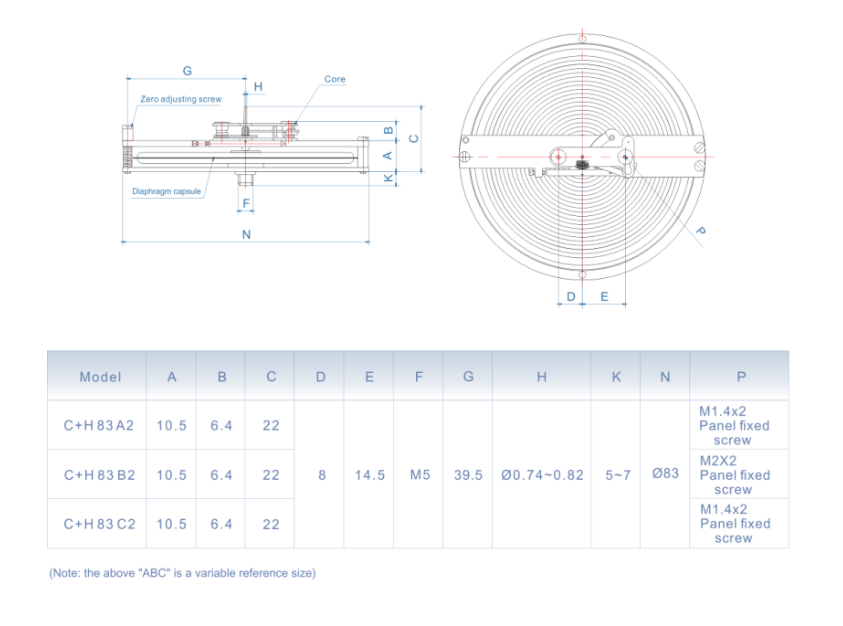
Calibration and Maintenance
Calibration and maintenance are critical aspects of cryogenic differential pressure gauge service. Regular calibration is necessary to ensure accuracy, which can be affected by factors such as temperature changes and mechanical wear. Facilities should establish a routine calibration schedule, following the manufacturer's recommendations. Maintenance also involves inspecting for leaks, verifying the integrity of seals and connections, and assessing the functionality of the gauge’s display and electronic components.
Safety Considerations
Handling cryogenic fluids can pose significant hazards, including frostbite, asphyxiation, and explosions. Therefore, proper training for personnel working with these gauges is essential. Operators must understand the specific operational limits of the gauges and follow all safety protocols when performing maintenance or troubleshooting. Safety devices, such as pressure relief valves, should always be in place to prevent overpressure incidents.
Conclusion
In summary, cryogenic differential pressure gauges are critical instruments that ensure the safe and efficient operation of cryogenic systems. Their unique design and construction address the challenges posed by low-temperature environments, and regular calibration and maintenance are essential to sustain their accuracy and reliability. By understanding the intricacies involved in their service, industries can bolster their operational safety and efficiency, thereby enhancing overall productivity.
-
High-Precision 5 Valve Manifold Differential Pressure Gauge Suppliers
NewsApr.29,2025
-
High-Precision Diaphragm Vacuum Pressure Gauges Manufacturers & Quotes
NewsApr.29,2025
-
Omega Differential Pressure Gauges High Accuracy & Durability
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Low Pressure Differential Pressure Gauges Precision Solutions & Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Digital Diaphragm Pressure Gaauge Precision Measurement & OEM Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Differential Pressure Gauge China Price High-Accuracy & Best Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
