
Nov . 01, 2024 11:36 Back to list
Understanding the Distinction Between Differential and Absolute Pressure Measurement Devices
Understanding the Difference Between Differential and Absolute Pressure Gauges
Pressure measurement is a critical aspect in various industrial, scientific, and engineering applications. Two common types of pressure gauges used are differential pressure gauges and absolute pressure gauges. Each serves its specific purpose, and understanding their differences is essential for selecting the appropriate measurement tool for any application.
Definition of Pressure Types
Absolute Pressure is the measurement of pressure relative to a perfect vacuum. It means that absolute pressure gauges measure the pressure above a complete vacuum, which is 0 psi (pounds per square inch) at absolute zero pressure. This type of measurement is useful in applications where precise pressure readings are required, such as in meteorology, vacuum systems, and barometric measurements.
On the other hand, Differential Pressure refers to the difference in pressure between two points. Differential pressure gauges measure the pressure difference between a reference point (often atmospheric pressure) and the pressure within a system or between two points within the same system. This kind of measurement is essential in applications such as flow measurement, filtration monitoring, and HVAC systems, where the pressure drop across an element needs to be evaluated.
Key Differences
difference between differential and absolute pressure gauges
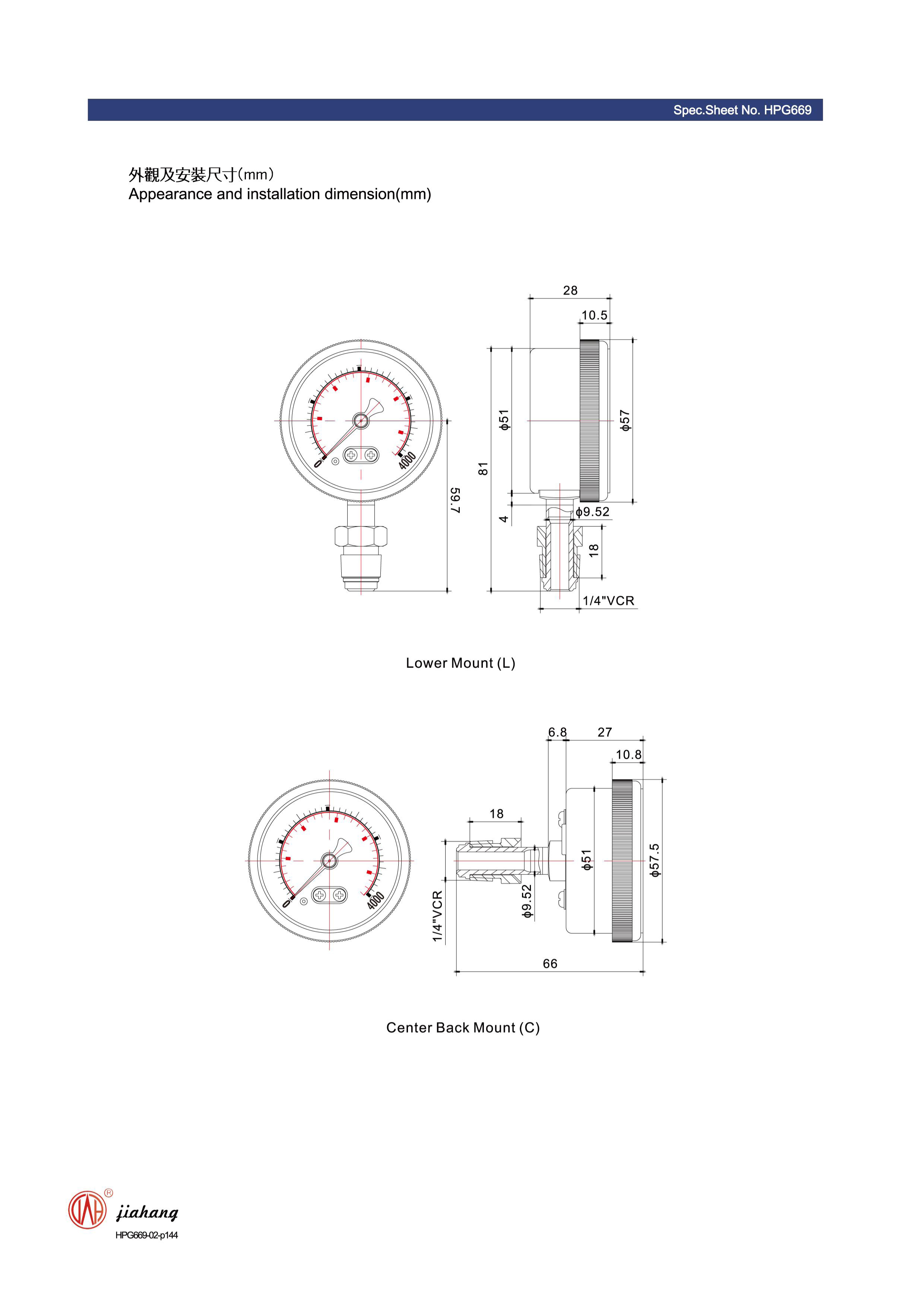
1. Reference Point One of the most significant differences between the two types of gauges lies in their reference points. Absolute pressure gauges reference a vacuum, providing a reading that indicates the total pressure exerted by a gas or liquid. In contrast, differential gauges compare two pressure points, often one of which is atmospheric pressure. This means that the readings can fluctuate based on changes in the atmospheric pressure when measuring with differential gauges.
2. Applications The choice between using an absolute or differential pressure gauge often hinges on the application. Absolute pressure gauges are typically employed in environments where knowing the absolute pressure is vital, such as in high-altitude aviation or deep-sea applications where ambient pressure changes dramatically. Conversely, differential pressure gauges are more commonly used in processes where flow rates and pressure changes across equipment are monitored, like in filter applications or in managing airflow in ventilation systems.
3. Measurement Range Absolute pressure gauges generally measure over a larger range compared to differential gauges. Because they start at absolute zero, they can measure tiny variations in pressure effectively, while differential gauges may have limitations based on the two pressure points they compare.
4. Calibration Calibration processes also differ between the two types. Absolute gauges are calibrated with respect to a known vacuum standard, while differential gauges require careful consideration of both reference points to ensure accurate readings.
Conclusion
In summary, the choice between using a differential pressure gauge and an absolute pressure gauge depends on the specific measurement needs. Understanding the fundamental differences ensures that engineers and technicians can select the right tool for accurate pressure readings, ultimately leading to more efficient and effective system management. By appreciating the applications, reference points, and measurement ranges of these gauges, users can significantly enhance their measurement strategies.
-
High-Precision 5 Valve Manifold Differential Pressure Gauge Suppliers
NewsApr.29,2025
-
High-Precision Diaphragm Vacuum Pressure Gauges Manufacturers & Quotes
NewsApr.29,2025
-
Omega Differential Pressure Gauges High Accuracy & Durability
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Low Pressure Differential Pressure Gauges Precision Solutions & Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Digital Diaphragm Pressure Gaauge Precision Measurement & OEM Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Differential Pressure Gauge China Price High-Accuracy & Best Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
