
Dec . 05, 2024 16:46 Back to list
Understanding the Functionality and Applications of Differential Pressure Gauges
Understanding Differential Pressure Gauges Importance and Applications
In various industrial settings, understanding pressure differences is crucial for the efficient and safe operation of processes. One of the key instruments used to measure these pressure differentials is the differential pressure gauge. This device plays a significant role in monitoring and controlling systems across multiple sectors, including manufacturing, HVAC, and chemical processing.
What is a Differential Pressure Gauge?
A differential pressure gauge is an instrument that measures the difference in pressure between two points in a system. It typically consists of two input ports one for high pressure and one for low pressure. The gauge outputs a reading that indicates the differential pressure between these two points, usually represented in units such as pascals (Pa), inches of water column, or psi (pounds per square inch).
These gauges operate based on various sensing technologies, including mechanical methods (like diaphragms and Bourdon tubes), electronic sensors, and even advanced digital technologies. The choice of technology often depends on the application requirements, including accuracy, range, and environmental conditions.
Applications of Differential Pressure Gauges
1. HVAC Systems In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, differential pressure gauges are essential for ensuring optimal airflow and system efficiency. They help in monitoring filters, fan performance, and duct pressure balance, allowing for timely maintenance and adjustments.
2. Filtration Processes Differential pressure is a critical parameter in filtration systems. By measuring the pressure drop across filters, operators can determine when a filter is becoming clogged and needs cleaning or replacement. This ensures consistent performance and prolongs the lifespan of the filtration equipment.
3. Pump and Valve Monitoring Differential pressure gauges are widely used to monitor the performance of pumps and valves. By measuring pressure differences, operators can detect issues like cavitation or valve leakage, preventing costly damage and downtime.
differential pressure gauge p& quotes
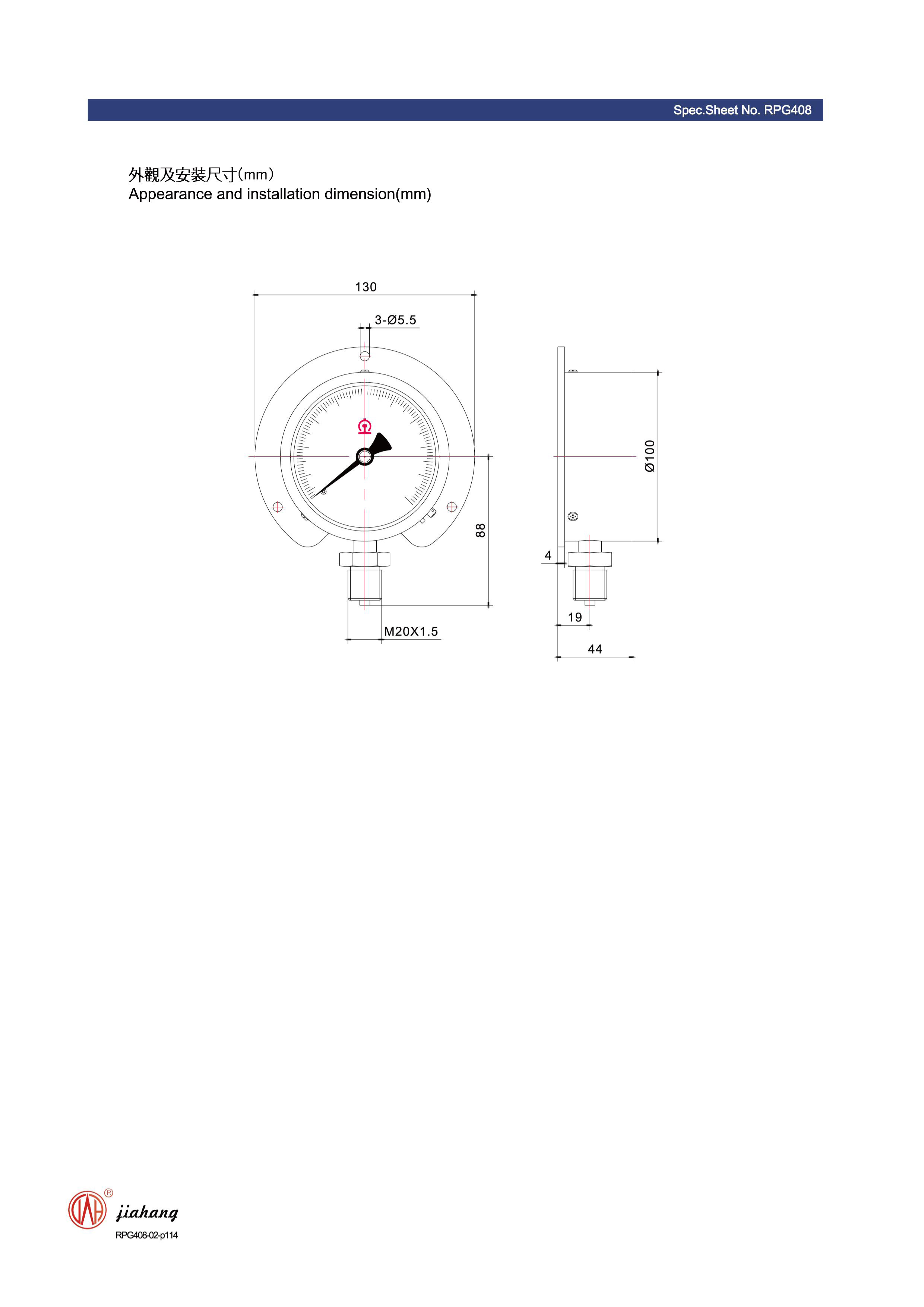
4. Chemical Processing In the chemical industry, differential pressure measurements are vital for the safe operation of reactors and tanks. These gauges can help monitor changes in process conditions, ensuring that reactions proceed safely and efficiently.
5. Cleanroom and Pharmaceutical Applications Maintaining pressure differentials in cleanrooms is critical for contamination control. Differential pressure gauges provide real-time monitoring to ensure that cleanrooms are operating within specified parameters, safeguarding product quality and compliance with regulatory standards.
Benefits of Using Differential Pressure Gauges
- Enhanced Safety By continuously monitoring pressure differences, these gauges help detect potential issues within systems before they escalate into dangerous situations. - Improved Efficiency Regular monitoring of differential pressure can lead to significant improvements in system efficiency. For instance, timely filter changes and optimal airflow management can save energy costs and enhance overall performance.
- Cost-Effectiveness While there may be an initial investment in high-quality differential pressure gauges, the long-term savings due to increased operational efficiency and reduced maintenance costs justify the expense.
- Versatility Differential pressure gauges can be used across a wide range of industries and applications, making them invaluable tools in various operational settings.
Conclusion
Differential pressure gauges are essential instruments in modern industrial operations. Their ability to accurately measure pressure differences empowers organizations to maintain operational efficiency, ensure safety, and manage system integrity effectively. As industries continue to evolve and demand more sophisticated monitoring solutions, the role of differential pressure gauges will only become more critical in achieving optimal performance and reliability. Whether in HVAC systems, filtration processes, or chemical processing, understanding and utilizing these gauges can lead to significant benefits across numerous applications.
-
High-Precision 5 Valve Manifold Differential Pressure Gauge Suppliers
NewsApr.29,2025
-
High-Precision Diaphragm Vacuum Pressure Gauges Manufacturers & Quotes
NewsApr.29,2025
-
Omega Differential Pressure Gauges High Accuracy & Durability
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Low Pressure Differential Pressure Gauges Precision Solutions & Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Digital Diaphragm Pressure Gaauge Precision Measurement & OEM Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Differential Pressure Gauge China Price High-Accuracy & Best Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
