
Dec . 07, 2024 15:58 Back to list
differential pressure gauge types factories
Understanding Differential Pressure Gauge Types and Their Applications
Differential pressure gauges are critical instruments used in various industrial applications to measure the pressure difference between two points in a system. These devices are essential in monitoring and controlling processes in industries such as oil and gas, water treatment, HVAC, pharmaceuticals, and many others. With advancements in technology, different types of differential pressure gauges have been developed, each tailored for specific applications and environments. In this article, we will explore the types of differential pressure gauges, their working principles, manufacturing considerations, and applications.
Types of Differential Pressure Gauges
1. Bourdon Tube Gauges Bourdon tube differential pressure gauges are one of the most traditional types. They function on the principle that a curved tube tends to straighten when pressure is applied. As the pressure differential increases, the movement of the tube is translated into a dial reading, indicating the pressure difference. These gauges are durable and suitable for various fluids and gases, making them a popular choice in many industries.
2. Diaphragm Gauges Diaphragm-type differential pressure gauges employ a thin, flexible membrane (diaphragm) that deflects under pressure. The movement of the diaphragm is linked to a mechanical or electronic transducer that converts the physical displacement into an electrical signal that can be read digitally. These gauges are particularly useful for low-pressure measurements and are often used in applications involving corrosive or viscous fluids.
3. Capacitive Gauges Capacitive differential pressure gauges utilize the capacitance change due to the displacement of a diaphragm. As the pressure differential changes, the diaphragm moves, altering the capacitance between two electrodes. This change is measured and displayed as a pressure reading. Capacitive gauges are known for their high precision and are often employed in laboratory settings or sensitive industries where accurate pressure measurements are critical.
4. Piezoelectric Gauges Piezoelectric differential pressure gauges take advantage of the piezoelectric effect, where certain materials generate an electric charge when mechanically stressed. These gauges are particularly suited for dynamic pressure measurements and can respond quickly to changes in pressure. They are extensively used in applications involving rapid fluctuations in pressure, such as in combustion engines and aerodynamic testing.
5. Digital Differential Pressure Gauges With the rise of digital technology, digital differential pressure gauges have become increasingly popular. These gauges often combine various sensing technologies, including piezoelectric and capacitive methods, to provide highly accurate readings. They typically feature user-friendly interfaces, wireless connectivity, and data logging capabilities, making them suitable for modern industrial environments where real-time monitoring and reduced downtime are essential.
differential pressure gauge types factories
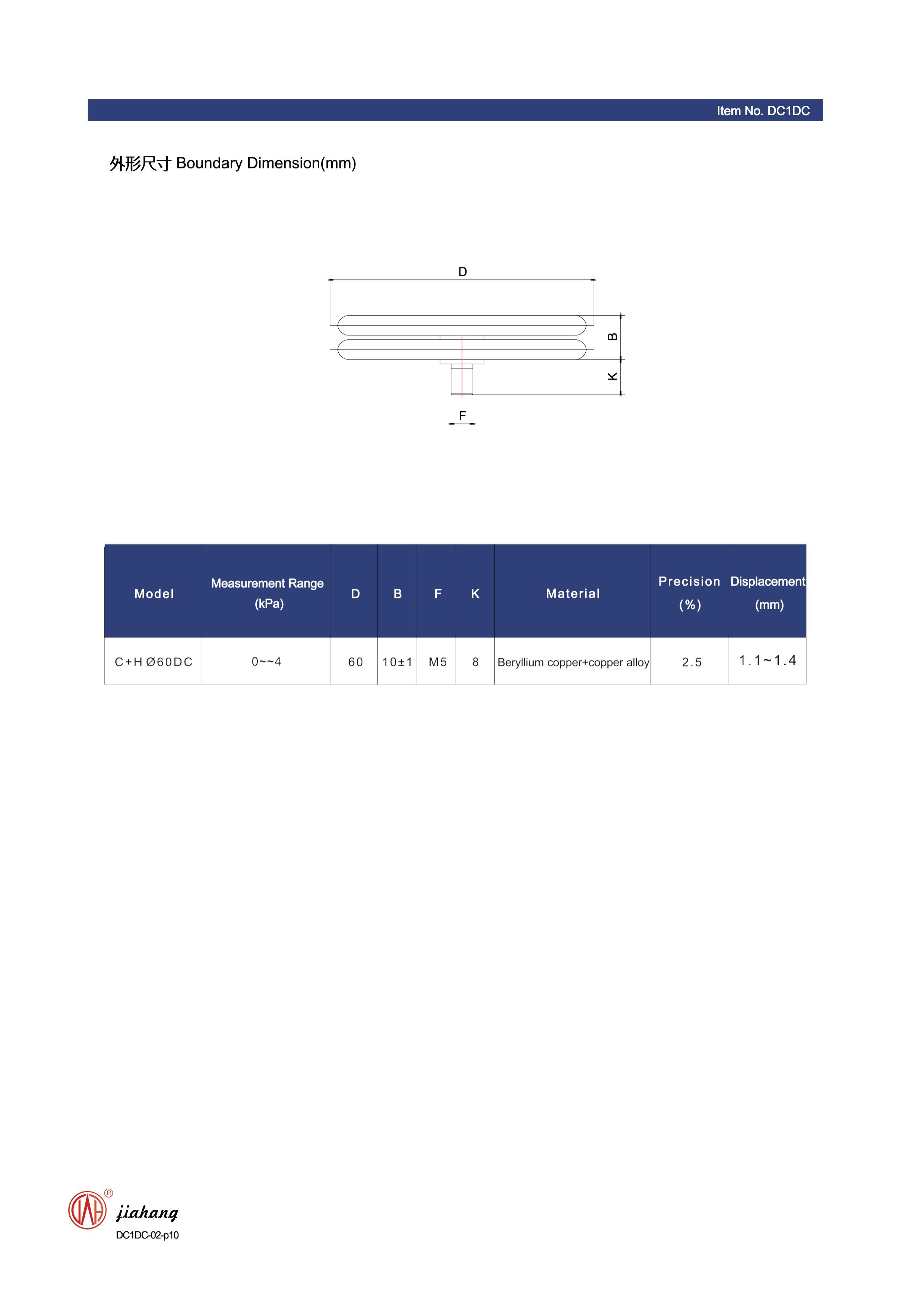
Manufacturing Considerations
The manufacturing of differential pressure gauges involves careful selection of materials to ensure durability and accuracy. Common materials include stainless steel, aluminum, and various polymers that can withstand harsh operating conditions. Manufacturers must also pay attention to calibration and quality control processes to ensure that the gauges provide reliable readings throughout their operational lifetime.
Applications
Differential pressure gauges find widespread applications in various fields. In water treatment plants, they are used to monitor filter performance, indicating when a filter needs to be cleaned or replaced. In HVAC systems, differential gauges help maintain optimal airflow by monitoring duct pressure differences. In the oil and gas industry, they are essential for monitoring pipelines and ensuring safe operation.
In pharmaceuticals, precise differential pressure measurements are critical for maintaining sterile environments in production areas. Thus, differential pressure gauges play an indispensable role in ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Conclusion
Differential pressure gauges are vital instruments in modern industry, with various types suited to different applications. Understanding the unique features and working principles of each type enables manufacturers and operators to select the appropriate gauge for their specific needs, ensuring efficiency, safety, and reliability in their operations. As technology continues to evolve, the capabilities and applications of differential pressure gauges will undoubtedly expand, leading to even greater innovations in industrial measurement solutions.
-
High-Precision 5 Valve Manifold Differential Pressure Gauge Suppliers
NewsApr.29,2025
-
High-Precision Diaphragm Vacuum Pressure Gauges Manufacturers & Quotes
NewsApr.29,2025
-
Omega Differential Pressure Gauges High Accuracy & Durability
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Low Pressure Differential Pressure Gauges Precision Solutions & Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Digital Diaphragm Pressure Gaauge Precision Measurement & OEM Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Differential Pressure Gauge China Price High-Accuracy & Best Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
