
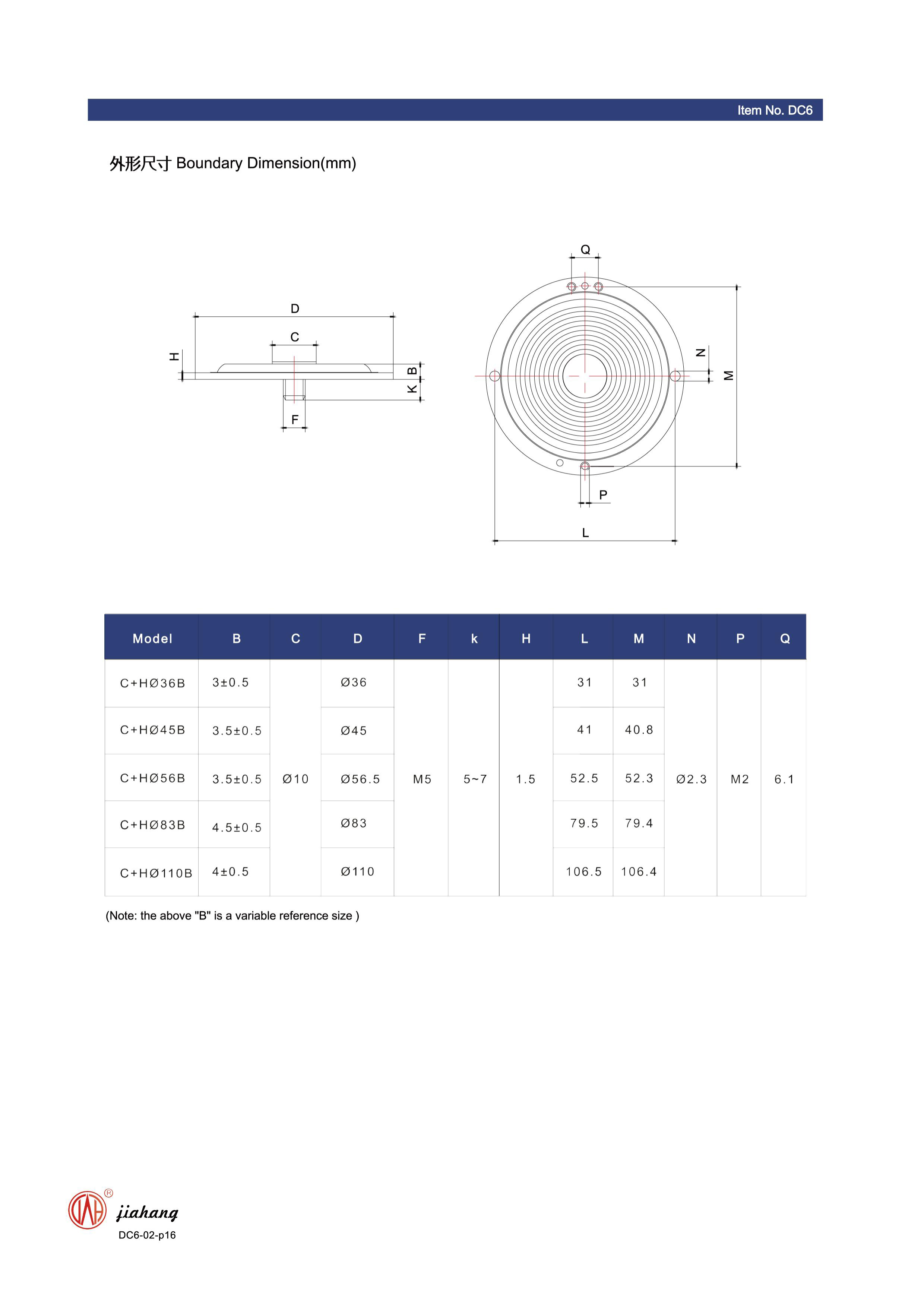
Nov . 11, 2024 01:13 Back to list
Magnetic Differential Pressure Gauge Manufacturing and Performance Insights for Industry Applications
Overview of Magnetic Differential Pressure Gauges
Magnetic differential pressure gauges are essential instruments used in various industries to measure the pressure difference between two points in a system. These gauges are particularly valuable in applications involving liquids, gases, and vapors, where precise monitoring is crucial for efficiency, safety, and performance. This article delves into the functionality, advantages, and applications of magnetic differential pressure gauges, as well as insights into their manufacturing considerations.
Understanding the Functionality
A magnetic differential pressure gauge operates based on the principle of magnetic force, which provides a highly accurate means of measuring pressure differentials. Unlike traditional mechanical gauges that rely on diaphragms or bellows, magnetic gauges utilized a more robust design with minimal moving parts. This design enhances reliability and longevity, making them suitable for harsh environments.
When pressure is applied at two input points, it creates a force that actuates the gauge mechanism, usually a float or ball within a tube filled with a magnetic fluid. The movement of this float correlates directly with the pressure difference, which is then translated into a readable output, usually in the form of a dial or digital reading. This mechanism ensures that the gauge can respond quickly to changes in pressure, providing real-time data that is critical in many industrial processes.
Advantages of Magnetic Differential Pressure Gauges
One of the primary advantages of magnetic differential pressure gauges is their durability. The absence of delicate mechanical components reduces wear and tear, minimizing maintenance requirements and downtime. Furthermore, these gauges can operate over a wide range of temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for various applications, from water treatment to oil and gas production.
Another significant benefit is their accuracy. Magnetic gauges offer high precision, allowing operators to make informed decisions based on reliable data. This accuracy is vital for processes requiring stringent pressure control, such as chemical manufacturing and pharmaceuticals, where even minor fluctuations can lead to significant operational issues or safety risks.
Additionally, magnetic differential pressure gauges are often immune to common issues faced by traditional gauges, such as vibration and shock. Their robust design allows them to function effectively in harsh environments, including those with excessive dust, moisture, or corrosive substances.
magnetic differential pressure gauge factory
Applications
Magnetic differential pressure gauges find applications across a broad spectrum of industries. In the oil and gas sector, they monitor pressure levels in pipelines and storage tanks, ensuring safe operations and preventing leaks. In HVAC systems, these gauges help manage air pressure distribution, essential for maintaining proper airflow and energy efficiency.
In the water treatment industry, magnetic gauges are employed to monitor filtration systems, ensuring optimal filter performance by measuring the pressure differential across the filter medium. This helps in determining when a filter needs to be replaced or cleaned, thus prolonging its lifespan and maintaining water quality.
In the pharmaceutical and food industries, maintaining sterile conditions is vital. Magnetic differential pressure gauges are used to monitor the pressure in clean rooms and storage facilities, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and safeguarding product integrity.
Manufacturing Considerations
When considering the manufacturing of magnetic differential pressure gauges, several factors come into play. The choice of materials is crucial; manufacturers typically use stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials to ensure durability and longevity. Additionally, precision engineering is required to ensure the gauge's response time and accuracy meet industry standards.
Quality control plays a significant role in the manufacturing process. Rigorous testing is conducted to confirm that each gauge can withstand its advertised operating conditions, ensuring reliability in the field. Manufacturers must also stay abreast of industry innovations, integrating advanced technology into their designs to enhance functionality and user experience.
Conclusion
Magnetic differential pressure gauges are invaluable tools that contribute to operational efficiency and safety across numerous industries. Their robust design, accuracy, and resistance to harsh conditions make them a preferred choice for various applications. As technology advances, continued innovation in the manufacturing of these gauges will further enhance their performance and reliability, meeting the ever-evolving needs of industries worldwide.
-
High-Precision 5 Valve Manifold Differential Pressure Gauge Suppliers
NewsApr.29,2025
-
High-Precision Diaphragm Vacuum Pressure Gauges Manufacturers & Quotes
NewsApr.29,2025
-
Omega Differential Pressure Gauges High Accuracy & Durability
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Low Pressure Differential Pressure Gauges Precision Solutions & Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Digital Diaphragm Pressure Gaauge Precision Measurement & OEM Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Differential Pressure Gauge China Price High-Accuracy & Best Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
