
lis . 15, 2024 16:46 Back to list
solid front differential pressure gauge company
Understanding Solid Front Differential Pressure Gauges A Comprehensive Overview
In various industrial applications, the measurement and monitoring of pressure are crucial for safety, efficiency, and reliability. One of the tools that have gained significant attention in this field is the solid front differential pressure gauge. This article delves into what these gauges are, how they function, their applications, and the advantages they offer.
What is a Solid Front Differential Pressure Gauge?
A solid front differential pressure gauge is a specialized instrument designed to measure the difference in pressure between two points within a system. Unlike standard gauges, which can have vulnerable glass fronts, solid front gauges are built with a robust, solid front construction that minimizes the risk of breakage, making them suitable for harsh environments. This feature enhances safety, particularly in applications where pressure fluctuations can lead to equipment damage or hazardous situations.
How Do They Work?
The mechanism of a solid front differential pressure gauge is quite straightforward. It utilizes a sensing element, typically a diaphragm or a bellows, which responds to the pressure difference between the two ports connected to the system. As the pressure changes, the sensing element deflects, and this motion is translated into a rotational movement, which is then displayed on the gauge’s dial.
The solid front design means that the gauge can withstand high pressures and prevent any potential injuries that might result from a shattered gauge face in the event of a pressure surge. This is particularly important in industries where extreme conditions can prevail, such as oil and gas, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals.
Applications of Solid Front Differential Pressure Gauges
Solid front differential pressure gauges are utilized across a wide range of industries
1. Oil and Gas These gauges monitor pressure differentials in pipelines and storage systems, ensuring that operations remain within safe limits. 2. Water Treatment In water treatment facilities, they are used to measure pressure differences across filters and membranes, helping to optimize performance and detect blockages.
3. HVAC Systems In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, differential pressure gauges help maintain proper airflow by measuring pressure differences across air filters.
solid front differential pressure gauge company
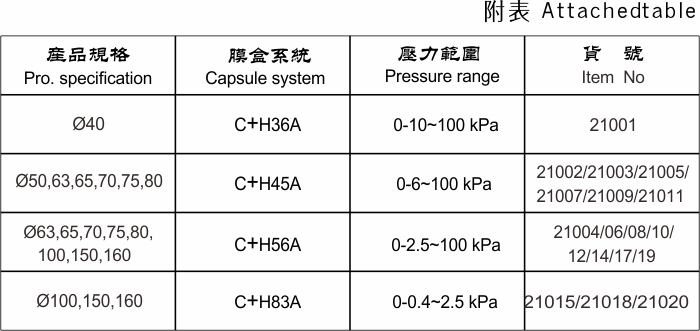
4. Pharmaceuticals Ensuring sterile environments is critical in pharmaceutical manufacturing. These gauges monitor pressure in cleanrooms and throughout various processes to ensure compliance with safety standards.
5. Manufacturing Many manufacturing processes rely on maintaining specific pressure levels. Solid front differential pressure gauges provide real-time monitoring, allowing for immediate adjustments.
Advantages of Solid Front Differential Pressure Gauges
1. Safety The solid front reduces the risk of injury or accidents caused by broken glass, making these gauges safer to use in challenging environments.
2. Durability Built to withstand harsh conditions, solid front differential pressure gauges can endure extreme pressures, ensuring longevity and reliability.
3. Accuracy These gauges provide precise measurements of pressure differentials, which are crucial for process optimization and maintenance.
4. Versatility With various design options and configurations, solid front differential pressure gauges can be adapted to fit numerous applications across different industries.
5. Ease of Reading Many solid front gauges are designed with clear dials and intuitive scaling, making it easy for operators to monitor conditions at a glance.
Conclusion
Solid front differential pressure gauges play an essential role in various industrial applications, providing reliable and accurate measurements critical for maintaining safety and efficiency. Their robust design offers advantages in durability and safety that standard gauges cannot match. As industries continue to prioritize safety and efficiency, the use of solid front differential pressure gauges is likely to grow, affirming their value in workplace settings and ensuring that operations run smoothly and safely. Understanding this technology is fundamental for professionals seeking to enhance their systems' reliability and performance.
-
High-Precision 5 Valve Manifold Differential Pressure Gauge Suppliers
NewsApr.29,2025
-
High-Precision Diaphragm Vacuum Pressure Gauges Manufacturers & Quotes
NewsApr.29,2025
-
Omega Differential Pressure Gauges High Accuracy & Durability
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Low Pressure Differential Pressure Gauges Precision Solutions & Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Digital Diaphragm Pressure Gaauge Precision Measurement & OEM Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Differential Pressure Gauge China Price High-Accuracy & Best Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
