
Июн . 13, 2024 11:02 Back to list
Measuring device for mass, precision pressure gauge, and accuracy in force assessment.
Understanding the Role of Mass, Precision, and Pressure Gauges in Industrial Applications
In the realm of industrial processes and scientific measurements, the concepts of mass, precision, and pressure gauges hold paramount importance. These elements not only ensure operational efficiency but also contribute significantly to safety and accuracy in various applications.
Mass, a fundamental physical quantity representing the amount of matter in an object, is a critical parameter in numerous industries. It forms the basis for many calculations, especially in chemistry where precise mass measurements are essential for accurate reactions. High-precision balances are used to measure mass, ensuring minimal errors and consistent results. In manufacturing, mass measurements are vital for quality control, ensuring products meet specific weight requirements.
Precision, on the other hand, refers to the level of detail and accuracy in a measurement. It is a crucial aspect in any scientific or engineering endeavor, particularly when dealing with delicate operations or high-stakes decisions. Precision instruments like pressure gauges play a significant role in maintaining this level of accuracy.
Pressure gauges, a staple in industrial settings, are designed to measure the force exerted by a fluid or gas on a surface area. They come in various types, including absolute, gauge, and differential pressure gauges, each tailored to specific applications They come in various types, including absolute, gauge, and differential pressure gauges, each tailored to specific applications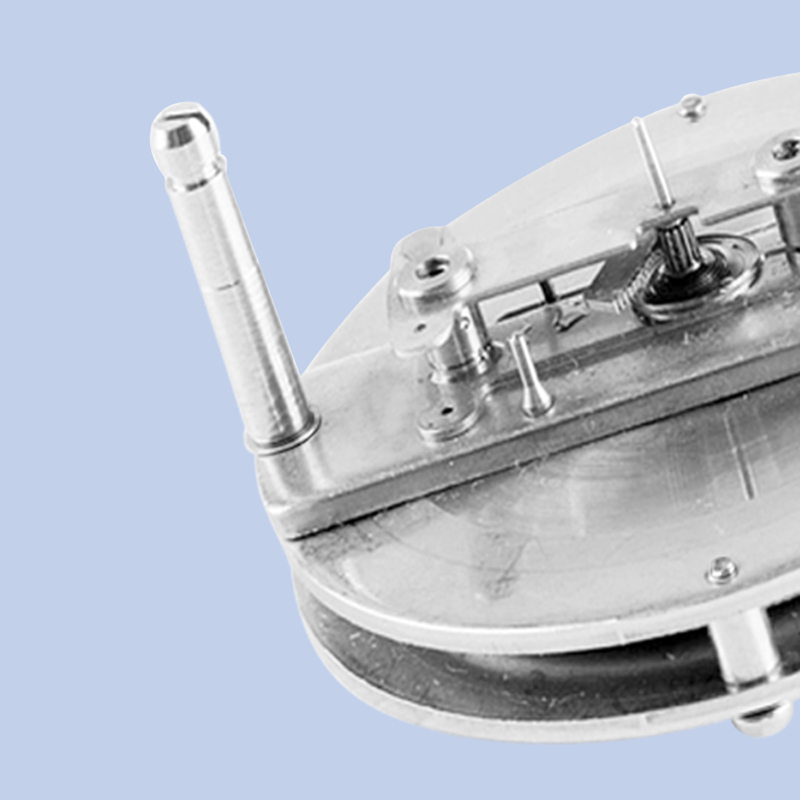 They come in various types, including absolute, gauge, and differential pressure gauges, each tailored to specific applications They come in various types, including absolute, gauge, and differential pressure gauges, each tailored to specific applications
They come in various types, including absolute, gauge, and differential pressure gauges, each tailored to specific applications They come in various types, including absolute, gauge, and differential pressure gauges, each tailored to specific applications mass precision pressure gauge. For instance, in the oil and gas industry, pressure gauges monitor pipeline pressures to prevent explosions, while in the medical field, they are used to measure blood pressure with utmost precision.
The precision of these pressure gauges is often determined by their sensitivity and resolution, which can be influenced by factors such as temperature, calibration, and mechanical shock. Regular maintenance and calibration are necessary to maintain the precision of these instruments, ensuring they provide reliable data for decision-making.
Innovations in technology have led to the development of digital pressure gauges that offer higher precision and accuracy compared to their analog counterparts. These digital devices often come equipped with features like data logging, alarm settings, and wireless connectivity, enhancing the overall monitoring process.
In conclusion, the interplay between mass, precision, and pressure gauges is a testament to the intricate balance that drives successful industrial operations. The accurate measurement of mass ensures consistency in production, while precision pressure gauges provide the necessary data for safe and efficient system management. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more advanced tools to enhance these measurements, further cementing their importance in our modern world.
mass precision pressure gauge. For instance, in the oil and gas industry, pressure gauges monitor pipeline pressures to prevent explosions, while in the medical field, they are used to measure blood pressure with utmost precision.
The precision of these pressure gauges is often determined by their sensitivity and resolution, which can be influenced by factors such as temperature, calibration, and mechanical shock. Regular maintenance and calibration are necessary to maintain the precision of these instruments, ensuring they provide reliable data for decision-making.
Innovations in technology have led to the development of digital pressure gauges that offer higher precision and accuracy compared to their analog counterparts. These digital devices often come equipped with features like data logging, alarm settings, and wireless connectivity, enhancing the overall monitoring process.
In conclusion, the interplay between mass, precision, and pressure gauges is a testament to the intricate balance that drives successful industrial operations. The accurate measurement of mass ensures consistency in production, while precision pressure gauges provide the necessary data for safe and efficient system management. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more advanced tools to enhance these measurements, further cementing their importance in our modern world.
 They come in various types, including absolute, gauge, and differential pressure gauges, each tailored to specific applications They come in various types, including absolute, gauge, and differential pressure gauges, each tailored to specific applications
They come in various types, including absolute, gauge, and differential pressure gauges, each tailored to specific applications They come in various types, including absolute, gauge, and differential pressure gauges, each tailored to specific applications mass precision pressure gauge. For instance, in the oil and gas industry, pressure gauges monitor pipeline pressures to prevent explosions, while in the medical field, they are used to measure blood pressure with utmost precision.
The precision of these pressure gauges is often determined by their sensitivity and resolution, which can be influenced by factors such as temperature, calibration, and mechanical shock. Regular maintenance and calibration are necessary to maintain the precision of these instruments, ensuring they provide reliable data for decision-making.
Innovations in technology have led to the development of digital pressure gauges that offer higher precision and accuracy compared to their analog counterparts. These digital devices often come equipped with features like data logging, alarm settings, and wireless connectivity, enhancing the overall monitoring process.
In conclusion, the interplay between mass, precision, and pressure gauges is a testament to the intricate balance that drives successful industrial operations. The accurate measurement of mass ensures consistency in production, while precision pressure gauges provide the necessary data for safe and efficient system management. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more advanced tools to enhance these measurements, further cementing their importance in our modern world.
mass precision pressure gauge. For instance, in the oil and gas industry, pressure gauges monitor pipeline pressures to prevent explosions, while in the medical field, they are used to measure blood pressure with utmost precision.
The precision of these pressure gauges is often determined by their sensitivity and resolution, which can be influenced by factors such as temperature, calibration, and mechanical shock. Regular maintenance and calibration are necessary to maintain the precision of these instruments, ensuring they provide reliable data for decision-making.
Innovations in technology have led to the development of digital pressure gauges that offer higher precision and accuracy compared to their analog counterparts. These digital devices often come equipped with features like data logging, alarm settings, and wireless connectivity, enhancing the overall monitoring process.
In conclusion, the interplay between mass, precision, and pressure gauges is a testament to the intricate balance that drives successful industrial operations. The accurate measurement of mass ensures consistency in production, while precision pressure gauges provide the necessary data for safe and efficient system management. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more advanced tools to enhance these measurements, further cementing their importance in our modern world. Share
Latest news
-
High-Precision 5 Valve Manifold Differential Pressure Gauge Suppliers
NewsApr.29,2025
-
High-Precision Diaphragm Vacuum Pressure Gauges Manufacturers & Quotes
NewsApr.29,2025
-
Omega Differential Pressure Gauges High Accuracy & Durability
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Low Pressure Differential Pressure Gauges Precision Solutions & Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Digital Diaphragm Pressure Gaauge Precision Measurement & OEM Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Differential Pressure Gauge China Price High-Accuracy & Best Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
