
10 月 . 10, 2024 14:13 Back to list
famous differential pressure gauge diaphragm type
Understanding the Diaphragm-Type Differential Pressure Gauge
Differential pressure gauges are critical instruments in various industrial applications, serving to measure the difference in pressure between two points in a system. Among the various types of differential pressure gauges, the diaphragm-type gauge is one of the most famous due to its reliability, accuracy, and versatility. This article provides a detailed overview of diaphragm-type differential pressure gauges, including their design, operational principles, applications, and advantages.
Design and Working Principle
A diaphragm-type differential pressure gauge primarily consists of a flexible diaphragm that separates two pressure chambers. When pressure is applied to either side of the diaphragm, it flexes in response to the pressure difference. This displacement is then translated into a readable output, typically through a mechanical linkage to a pointer that moves along a calibrated scale.
The diaphragm is usually made from materials such as stainless steel, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), or elastomers, selected based on the application and the types of fluids being measured. The choice of materials is crucial to ensure compatibility with different media and to withstand corrosive or high-temperature environments.
As pressure is applied to one side of the diaphragm, it moves in proportion to the differential pressure. The mechanical displacement is converted into an electrical signal in some models, particularly those used in digital applications. This signal can then be displayed on a digital readout or transmitted to a control system for monitoring purposes. The precision with which the diaphragm flexes is key to the gauge's accuracy, making it a popular choice for many critical measurements.
Applications
Diaphragm-type differential pressure gauges are widely used across various industries, including
1. Oil and Gas They are often employed in pipeline monitoring to ensure safe transportation of fluids and to detect leakages by measuring pressure differences.
2. Chemical Processing These gauges help in monitoring processes where chemical reactions occur, ensuring that pressure remains within safe limits to prevent accidents.
famous differential pressure gauge diaphragm type
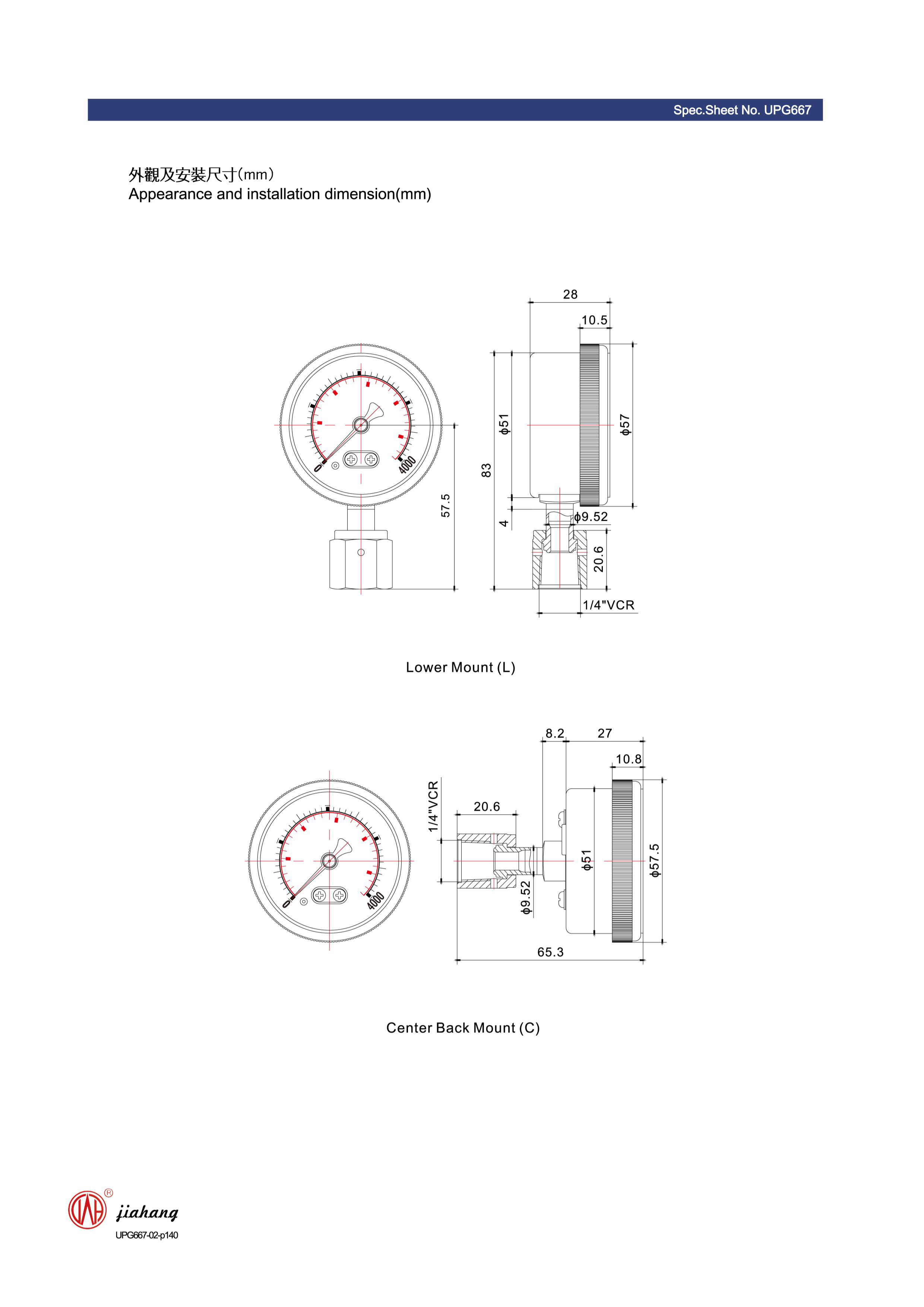
4. HVAC Systems In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, they measure pressure differences to regulate airflow and enhance system performance.
5. Pharmaceuticals In pharmaceutical manufacturing, maintaining accurate pressure differentials is crucial for sterility and safety. Diaphragm-type gauges provide reliable readings for these sensitive environments.
Advantages
The diaphragm-type differential pressure gauge boasts several advantages, making it a preferred choice in many applications
- Accuracy These gauges offer high precision, essential for processes requiring strict pressure control. - Sensitivity The flexible diaphragm allows these gauges to detect even small changes in pressure, making them suitable for various applications.
- Durability With sturdy construction, diaphragm-type gauges can endure harsh environmental conditions, including temperature fluctuations and corrosive substances.
- Minimal Maintenance The design is generally simple and robust, reducing the need for frequent maintenance or recalibration.
- Versatility They can be used for gases, liquids, and even slurries, providing flexibility across different industries.
Conclusion
In summary, diaphragm-type differential pressure gauges are integral components in various industrial applications, known for their accuracy, reliability, and versatility. Their ability to measure pressure differences with high sensitivity makes them indispensable in maintaining safe and efficient operations across multiple sectors. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for precise pressure monitoring solutions, like diaphragm-type gauges, is likely to increase, ensuring that these instruments will remain at the forefront of industrial measurement and control technologies.
-
High-Precision 5 Valve Manifold Differential Pressure Gauge Suppliers
NewsApr.29,2025
-
High-Precision Diaphragm Vacuum Pressure Gauges Manufacturers & Quotes
NewsApr.29,2025
-
Omega Differential Pressure Gauges High Accuracy & Durability
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Low Pressure Differential Pressure Gauges Precision Solutions & Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Digital Diaphragm Pressure Gaauge Precision Measurement & OEM Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
-
Differential Pressure Gauge China Price High-Accuracy & Best Quotes
NewsApr.28,2025
